Step by step how to draw lewis structures
The Lewis structure is a graphic representation of the distribution of electrons around atoms. The reason to learn to draw the Lewis structure is to predict the number and type of bonds formed around the atom. Lewis structures also help predict molecular geometry. Chemistry students are often confused by the model, but following an appropriate procedure, drawing a Lewis structure is an easy process. Please note that there are several different strategies to build a Lewis structure. These instructions outline Kelter's strategy of drawing the Lewis structure of the molecule.
Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
In this step we add the total number of valence electrons from all the atoms in the molecule.
Step 2: Find the number of electrons necessary to make the atom "happy".
An atom is considered "happy" when the outer shell of the atom is filled. Elements in the fourth period of the periodic table require eight electrons to fill the outer electron shell. This property is often known as the "octet rule".
Step 3: Determine the number of bonds in the molecule.
Covalent bonds are formed when one electron from each atom forms an electron pair. Step 2 shows the number of required electrons and Step 1 shows the number of electrons possessed. Subtracting the number in step 1 from the number in step 2 gives the number of electrons necessary to complete the octet. Since each bond formed requires two electrons, the number of bonds is half the number of electrons required.
Step 4: Select the central atom.
The central atom of the molecule is usually the most electronegative atom or the most valuable atom. To find electronegativity, refer to a table that relies on periodic table trends or enumerates electronegativity values. Electronegativity decreases to go down the group of the periodic table and tends to move from left to right over a period of time. Hydrogen atoms and halogen atoms tend to appear on the outside of the molecule and rarely are central atoms.
Step 5: Draw skeleton structure.
Connect the atom to the central atom with a straight line representing the bond between the two atoms. The central atom can have four other atoms attached to it.
Step 6: Place electrons outside the atom.
Complete octets around each of the outer atoms. If there is not enough electrons to complete the octet, the skeleton structure in Step 5 is incorrect. Please make another arrangement. Initially, this may cause errors on some trials. As you gain experience, it makes it easier to predict skeletal structure.
Step 7: Place the remaining electrons around the central atom.
Complete the remaining electron and octet of the central atom. If there are remaining bonds from step 3, make a double bond with an isolated pair on the outer atom. The double bond is represented by two solid lines drawn between pairs of atoms. If there are more than 8 electrons on the central atom and that atom is not one of the exceptions to the octet rule, it is possible that the number of valence atoms in Step 1 was erroneously counted.
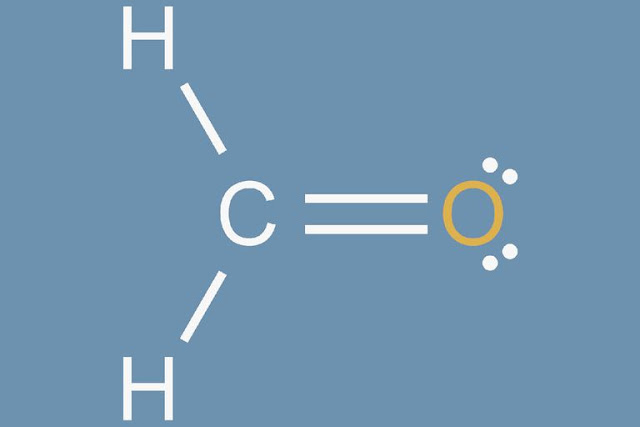
This completes the molecular Lewis dot structure. For examples of problems using this process, please make sure to draw the Lewis structure of formaldehyde.
This completes the molecular Lewis dot structure. For examples of problems using this process, please make sure to draw the Lewis structure of formaldehyde.
Lewis structure and real molecule
When you learn about valence, oxidation state, and bonding, the Lewis structure is useful, but there are many exceptions in the real world. The atom will try to fill the valence electron shell or fill half. However, atoms can form and form molecules that are ideally not stable. In some cases the central atom can form more than the other atoms attached to it. Also, the number of valence electrons may exceed 8, especially when the number of atoms is high. The Lewis structure is useful for light elements, but it is not very useful for transition metals including lanthanides and actinides. Students are careful not to remember that the Lewis structure is a valuable tool for knowing and predicting the behavior of atoms in a molecule, but it is an incomplete representation of actual electronic activity.
Main Activities of Lewis Structure
- The Lewis structure depicts the distribution of electrons around atoms.
- To draw a Lewis structure, add the number of valence electrons from all atoms, determine the number of electrons necessary to satisfy the octet rule, and find the number of chemical bonds in the molecule.
- Select atoms in the center and draw a skeleton structure around them.
- Finally, place electrons around the atom and complete the octet. The remaining atoms are placed around the central atom.
